Local government is the foundation of grassroots democracy in Punjab. It brings governance closer to citizens by handling day-to-day civic needs, local development, and community services. The Punjab local government system operates through elected bodies at urban and rural levels, ensuring participation, accountability, and efficient service delivery.
This article provides a neutral and educational explanation of the Punjab local government system, covering its structure, types of local bodies, roles, functions, and how it supports decentralized governance. The focus remains informational, without political opinions or debate.
Why Local Government Matters in Punjab
Local governments are essential because they directly impact citizens’ daily lives.
Key reasons local governance is important:
- Faster response to local issues
- Better understanding of community needs
- Citizen participation in decision-making
- Decentralized administration
Strong local governments improve service delivery and accountability.
Overview of the Punjab Local Government System
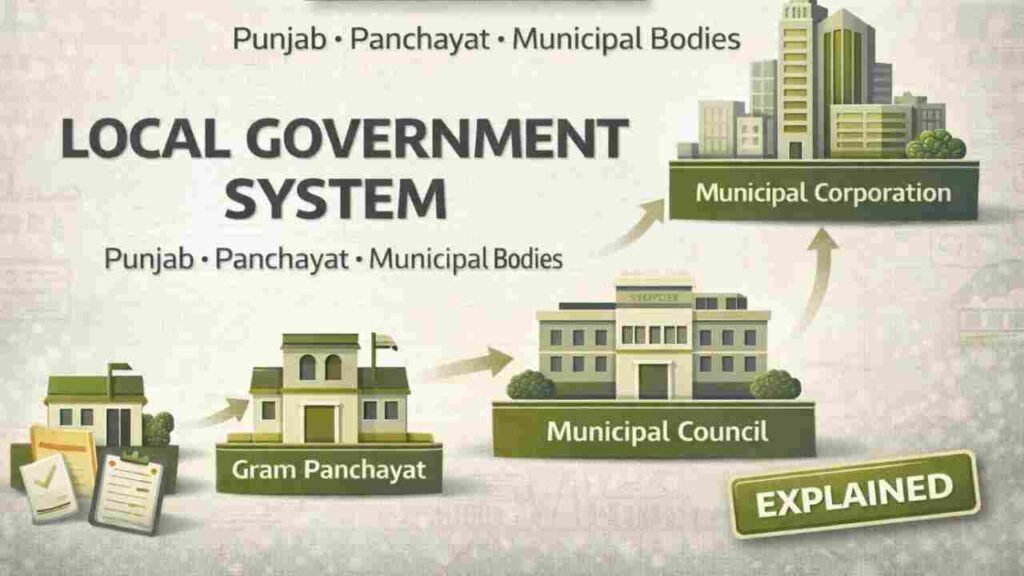
Punjab follows a structured local governance framework with urban and rural local bodies. These bodies function under constitutional provisions and state laws, with elected representatives and administrative support.
Broad components include:
- Urban Local Bodies
- Rural Local Bodies
- District-level coordination
Each level has defined responsibilities and functions.
Urban Local Bodies in Punjab
Urban local bodies manage civic administration in towns and cities.
Types of Urban Local Bodies
Urban governance in Punjab includes:
- Municipal Corporations
- Municipal Councils
- Nagar Panchayats
These bodies cater to different population sizes and urban needs.
Municipal Corporations
Municipal Corporations govern large cities.
Their responsibilities include:
- Urban planning and development
- Water supply and sanitation
- Road maintenance and street lighting
- Public health and cleanliness
They manage complex urban infrastructure.
Municipal Councils
Municipal Councils administer medium-sized towns.
Key functions include:
- Civic services
- Local infrastructure maintenance
- Regulation of markets and public spaces
They bridge the gap between rural and urban governance.
Nagar Panchayats
Nagar Panchayats govern areas transitioning from rural to urban.
Their role includes:
- Basic civic services
- Development planning
- Local regulation
They support gradual urbanization.
Rural Local Bodies in Punjab
Rural governance operates through the Panchayati Raj system.
Structure of Rural Local Government
Rural local bodies include:
- Gram Panchayat (village level)
- Panchayat Samiti (block level)
- Zila Parishad (district level)
This three-tier structure ensures representation at all levels.
Gram Panchayat
The Gram Panchayat is the basic unit of rural governance.
Responsibilities include:
- Village development works
- Maintenance of local assets
- Implementation of welfare programs
- Addressing community issues
It plays a direct role in villagers’ daily lives.
Panchayat Samiti
Panchayat Samitis operate at the block level.
Their functions include:
- Coordinating Gram Panchayats
- Implementing development schemes
- Supervising rural projects
They act as a link between villages and districts.
Zila Parishad
Zila Parishads function at the district level.
Key roles include:
- District-wide development planning
- Coordination among Panchayat Samitis
- Monitoring rural development programs
They ensure balanced development across districts.
Role of Elected Representatives
Local government bodies are led by elected representatives.
Their roles include:
- Representing community interests
- Participating in decision-making
- Ensuring accountability
Elections promote democratic participation at the grassroots level.
Administrative Support to Local Bodies
Local governments receive administrative support from officials.
Support includes:
- Implementation guidance
- Financial management
- Technical assistance
This support ensures efficient functioning.
Financial Resources of Local Governments
Local bodies require funds to deliver services.
Sources of revenue include:
- Government grants
- Local taxes and fees
- Development funds
Proper financial management supports sustainability.
Functions and Responsibilities of Local Governments
Local governments perform multiple functions.
Common responsibilities include:
- Water supply and sanitation
- Waste management
- Road maintenance
- Local infrastructure development
- Public health initiatives
These functions directly affect quality of life.
Importance of Decentralization
Decentralization strengthens governance by distributing authority.
Benefits include:
- Faster decision-making
- Better service delivery
- Increased citizen involvement
Decentralization is central to local governance.
Role of Local Government in Development
Local bodies contribute to development planning and execution.
Their role includes:
- Identifying local priorities
- Implementing development schemes
- Monitoring outcomes
Local insight improves development effectiveness.
Transparency and Accountability in Local Governance
Transparency builds public trust.
Measures include:
- Public meetings
- Open decision-making processes
- Financial reporting
Accountability ensures responsible governance.
Citizen Participation in Local Government
Citizen involvement strengthens local bodies.
Forms of participation include:
- Attending public meetings
- Providing feedback
- Community initiatives
Participation encourages shared responsibility.
Challenges Faced by Local Governments in Punjab
Local governments face operational challenges.
Common challenges include:
- Resource limitations
- Administrative coordination
- Capacity building needs
Addressing challenges improves effectiveness.
Use of Technology in Local Administration
Technology supports efficient governance.
Applications include:
- Digital record keeping
- Online service delivery
- Communication platforms
Technology enhances accessibility and transparency.
Coordination Between State and Local Governments
Coordination ensures smooth governance.
Coordination areas include:
- Policy implementation
- Resource allocation
- Monitoring and evaluation
Effective coordination avoids overlap.
Future Scope of Local Governance in Punjab
Local governance continues to evolve.
Future focus areas include:
- Capacity enhancement
- Improved financial autonomy
- Greater citizen engagement
Continuous improvement strengthens democracy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the purpose of local government in Punjab?
To manage local civic services and promote grassroots democracy.
Q2. How many levels of rural local government exist?
There are three levels: Gram Panchayat, Panchayat Samiti, and Zila Parishad.
Q3. Who governs urban areas in Punjab?
Municipal Corporations, Municipal Councils, and Nagar Panchayats.
Q4. Are local government members elected?
Yes. Members are elected by local residents.
Q5. Why is decentralization important?
It improves efficiency and citizen participation.
Conclusion
The Punjab local government system plays a vital role in delivering civic services, supporting development, and strengthening grassroots democracy. Through urban and rural local bodies, governance reaches communities directly, enabling responsive administration and citizen participation.
This article provides a clear and educational explanation of Punjab’s local government system, helping readers understand how local governance functions and why it is essential for effective administration.